Stream API
1. 思想
Stream流式思想类似于工厂车间的“生产流水线”,Stream流不是一种数据结构,不保存数据,而是对数据进行加工 处理。Stream可以看作是流水线上的一个工序。在流水线上,通过多个工序让一个原材料加工成一个商品
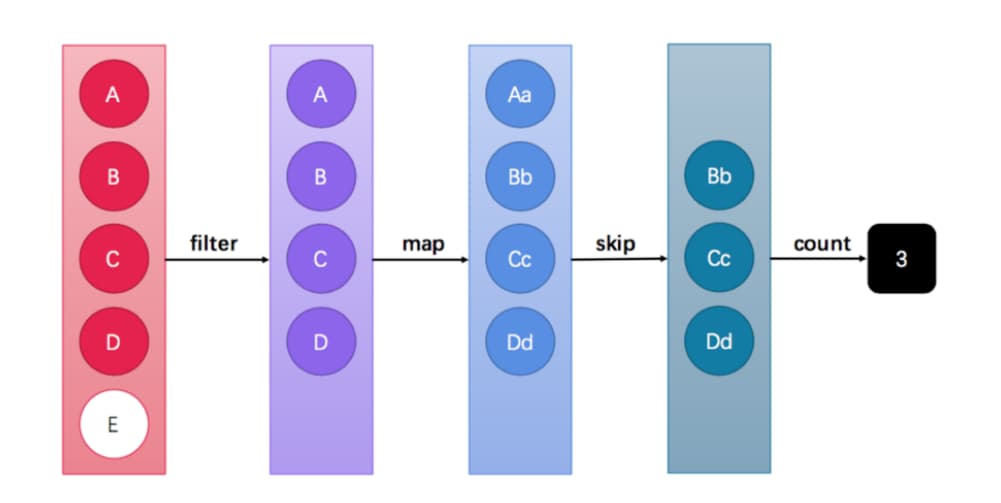
Stream API能让我们快速完成许多复杂的操作,如筛选、切片、映射、查找、去除重复,统计,匹配和归约
2. Stream流获取方式
2.1 根据Collection获取
首先,java.util.Collection 接口中加入了default方法 stream,也就是说Collection接口下的所有的实现都可以通过steam方法来获取Stream流
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.stream();
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.stream();
Vector vector = new Vector();
vector.stream();
}
是Map接口别没有实现Collection接口,那这时怎么办呢?这时我们可以根据Map获取对应的key value的集合
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Stream<String> stream = map.keySet().stream(); // key
Stream<Object> stream1 = map.values().stream(); // value
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Object>> stream2 = map.entrySet().stream(); //entry
}
2.2 通过Stream的of方法
在实际开发中我们不可避免的还是会操作到数组中的数据,由于数组对象不可能添加默认方法,所 有Stream接口中提供了静态方法of
public class StreamTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> a1 = Stream.of("a1", "a2", "a3");
String[] arr1 = {"aa","bb","cc"};
Stream<String> arr11 = Stream.of(arr1);
Integer[] arr2 = {1,2,3,4};
Stream<Integer> arr21 = Stream.of(arr2);
arr21.forEach(System.out::println);
// 注意:基本数据类型的数组是不行的
int[] arr3 = {1,2,3,4};
Stream.of(arr3).forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
3. Stream常用方法
| 方法名 | 方法作用 | 返回值类型 | 方法种类 |
|---|---|---|---|
| count | 统计个数 | long | 终结 |
| forEach | 逐一处理 | void | 终结 |
| filter | 过滤 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| limit | 取用前几个 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| skip | 跳过前几个 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| map | 映射 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
| concat | 组合 | Stream | 函数拼接 |
终结方法:返回值类型不再是Stream类型的方法,不再支持链式调用
非终结方法:返回值类型仍然是Stream类型的方法,支持链式调用
Stream注意事项(重要)
- Stream只能操作一次
- Stream方法返回的是新的流
- Stream不调用终结方法,中间的操作不会执行
3.1 foreach()-终结方法
forEach用来遍历流中的数据的
void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action);
Consumer是JDK8新特性的函数式接口,接受参数无返回参数
该方法接受一个Consumer接口,会将每一个流元素交给函数处理
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("a1", "a2", "a3").forEach(System.out::println);;
}
3.2 count-终结方法
Stream流中的count方法用来统计其中的元素个数的
long count();
该方法返回一个long值,代表元素的个数
public static void main(String[] args) {
long count = Stream.of("a1", "a2", "a3").count();
System.out.println(count);
}
3.3 filter
filter方法的作用是用来过滤数据的。返回符合条件的数据
可以通过filter方法将一个流转换成另一个子集流
Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate);
该接口接收一个Predicate函数式接口参数作为筛选条件
Predicate也是属于JDK8新特性里面的
public class my {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("a","ab","abc","b")
.filter(s -> s.contains("a")) // Lambda表达式简写小括号
.forEach(System.out::println);
//过滤偶数
Predicate<Integer> condition = num -> num % 2 == 0;
Stream.of(1,2,3,4,5)
.filter(condition)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
3.4 limit
limit方法可以对流进行截取处理,支取前n个数据
Stream<T> limit(long maxSize);
参数是一个long类型的数值,如果集合当前长度大于参数就进行截取,否则不操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("a1", "a2", "a3","bb","cc","aa","dd")
.limit(3)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.5 skip
如果希望跳过前面几个元素,可以使用skip方法获取一个截取之后的新流
Stream<T> skip(long n);
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("a1", "a2", "a3","bb","cc","aa","dd")
.skip(3)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.6 map
如果我们需要将流中的元素映射到另一个流中,可以使用map方法
<R> Stream<R> map(Function<? super T, ? extends R> mapper);
该接口需要一个Function函数式接口参数,可以将当前流中的T类型数据转换为另一种R类型的数据
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("1", "2", "3","4","5","6","7")
//.map(msg->Integer.parseInt(msg))
.map(Integer::parseInt) //转换为整数,变成新流
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.7 sorted
如果需要将数据排序,可以使用sorted方法:
Stream<T> sorted();
在使用的时候可以根据自然规则排序,也可以通过比较强来指定对应的排序规则
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("1", "3", "2","4","0","9","7")
.map(Integer::parseInt)
//.sorted() // 根据数据的自然顺序排序
.sorted((o1,o2)->o2-o1) // 根据比较强指定排序规则
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.8 distinct
如果要去掉重复数据,可以使用distinct方法
Stream<T> distinct();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream.of("1", "3", "3","4","0","1","7")
.map(Integer::parseInt)
.sorted((o1,o2)->o2-o1) // 根据比较强指定排序规则
.distinct() // 去掉重复的记录
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("--------");
Stream.of(
new Person("张三",18)
,new Person("李四",22)
,new Person("张三",18)
).distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.9 match-终结方法
如果需要判断数据是否匹配指定的条件,可以使用match相关的方法
boolean anyMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate); // 元素是否有任意一个满足条件
boolean allMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate); // 元素是否都满足条件
boolean noneMatch(Predicate<? super T> predicate); // 元素是否都不满足条件
使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean b = Stream.of("1", "3", "3", "4", "5", "1", "7")
.map(Integer::parseInt)
//.allMatch(s -> s > 0)
//.anyMatch(s -> s >4)
.noneMatch(s -> s > 4);
System.out.println(b);
}
3.10 find
如果我们需要找到某些数据,可以使用find方法来实现
Optional<T> findFirst();
Optional<T> findAny();
使用,涉及到了Optional类
public static void main(String[] args) {
Optional<String> first = Stream.of("1", "3", "3", "4", "5", "1",
"7").findFirst();
System.out.println(first.get());
Optional<String> any = Stream.of("1", "3", "3", "4", "5", "1",
"7").findAny();
System.out.println(any.get());
}
3.11 max和min
如果我们想要获取最大值和最小值,那么可以使用max和min方法
Optional<T> min(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
Optional<T> max(Comparator<? super T> comparator);
使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
Optional<Integer> max = Stream.of("1", "3", "3", "4", "5", "1", "7")
.map(Integer::parseInt)
.max((o1,o2)->o1-o2);
System.out.println(max.get());
Optional<Integer> min = Stream.of("1", "3", "3", "4", "5", "1", "7")
.map(Integer::parseInt)
.min((o1,o2)->o1-o2);
System.out.println(min.get());
}
3.12 reduce
如果需要将所有数据归纳得到一个数据,可以使用reduce方法
T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator);
使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer sum = Stream.of(4, 5, 3, 9)
// identity默认值
// 第一次的时候会将默认值赋值给x
// 之后每次会将 上一次的操作结果赋值给x y就是每次从数据中获取的元素
.reduce(0, (x, y) -> {
System.out.println("x="+x+",y="+y);
return x + y;
});
System.out.println(sum);
// 获取 最大值
Integer max = Stream.of(4, 5, 3, 9)
.reduce(0, (x, y) -> {
return x > y ? x : y;
});
System.out.println(max);
}
3.13 map和reduce的组合
Integer::sum
Java 中的 Integer sum() 方法
java.lang.Integer.sum() 是 java 中的一个内置方法,它返回其参数的总和。该方法根据 + 运算符将两个整数相加。
语法:
public static int sum(int a, int b)参数: 该方法接受两个要相互相加的参数:a :第一个整数值。b:第二个整数值。
**返回值:**该方法返回其参数的总和。
使用代码
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.求出所有年龄的总和
Integer sumAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).map(Person::getAge) // 实现数据类型的转换
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);
System.out.println(sumAge);
// 2.求出所有年龄中的最大值
Integer maxAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).map(Person::getAge) // 实现数据类型的转换,符合reduce对数据的要求
.reduce(0, Math::max); // reduce实现数据的处理
System.out.println(maxAge);
// 3.统计 字符 a 出现的次数
Integer count = Stream.of("a", "b", "c", "d", "a", "c", "a")
.map(ch -> "a".equals(ch) ? 1 : 0)
.reduce(0, Integer::sum);
System.out.println(count);
}
3.14 mapToInt
如果需要将Stream中的Integer类型转换成int类型,可以使用mapToInt方法来实现
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Integer占用的内存比int多很多,在Stream流操作中会自动装修和拆箱操作
Integer arr[] = {1,2,3,5,6,8};
Stream.of(arr)
.filter(i->i>0)
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("---------");
// 为了提高程序代码的效率,我们可以先将流中Integer数据转换为int数据,然后再操作
IntStream intStream = Stream.of(arr)
.mapToInt(Integer::intValue);
intStream.filter(i->i>3)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.15 concat
如果有两个流,希望合并成为一个流,那么可以使用Stream接口的静态方法concat
public static <T> Stream<T> concat(Stream<? extends T> a, Stream<? extends
T> b) {
Objects.requireNonNull(a);
Objects.requireNonNull(b);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Spliterator<T> split = new Streams.ConcatSpliterator.OfRef<>((Spliterator<T>) a.spliterator(), (Spliterator<T>)
b.spliterator());
Stream<T> stream = StreamSupport.stream(split, a.isParallel() ||
b.isParallel());
return stream.onClose(Streams.composedClose(a, b));
}
使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of("a","b","c");
Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of("x", "y", "z");
// 通过concat方法将两个流合并为一个新的流
Stream.concat(stream1,stream2).forEach(System.out::println);
}
3.16 综合使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("迪丽热巴", "宋远桥", "苏星河", "老子",
"庄子", "孙子", "洪七 公");
List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList("古力娜扎", "张无忌", "张三丰", "赵丽颖","张二狗", "张天爱", "张三");
// 1. 第一个队伍只保留姓名长度为3的成员
// 2. 第一个队伍筛选之后只要前3个人
Stream<String> stream1 = list1.stream().filter(s -> s.length() ==
3).limit(3);
// 3. 第二个队伍只要姓张的成员
// 4. 第二个队伍筛选之后不要前两个人
Stream<String> stream2 = list2.stream().filter(s ->
s.startsWith("张")).skip(2);
// 5. 将两个队伍合并为一个队伍
// 6. 根据姓名创建Person对象
// 7. 打印整个队伍的Person信息
Stream.concat(stream1,stream2)
//.map(n-> new Person(n))
.map(Person::new)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
4. Stream结果收集
4.1 结果收集到集合中
/**
* Stream结果收集
* 收集到集合中
*/
public void test01(){
// Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc");
List<String> list = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc","aa")
.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
// 收集到 Set集合中
Set<String> set = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa")
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(set);
// 如果需要获取的类型为具体的实现,比如:ArrayList HashSet
ArrayList<String> arrayList = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa")
//.collect(Collectors.toCollection(() -> new ArrayList<>()));
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
System.out.println(arrayList);
HashSet<String> hashSet = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa")
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
System.out.println(hashSet);
}
4.2 结果收集到数组中
Stream中提供了toArray方法来将结果放到一个数组中,返回值类型是Object[],如果我们要指定返回的 类型,那么可以使用另一个重载的toArray(IntFunction f)方法
/**
* Stream结果收集到数组中
*/
@Test
public void test02(){
Object[] objects = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa")
.toArray(); // 返回的数组中的元素是 Object类型
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(objects));
// 如果我们需要指定返回的数组中的元素类型
String[] strings = Stream.of("aa", "bb", "cc", "aa")
.toArray(String[]::new);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings));
}
4.3 对流中的数据做聚合计算
Java 8 Stream 的终极技巧——Collectors 操作 - 码农小胖哥 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
当我们使用Stream流处理数据后,可以像数据库的聚合函数一样对某个字段进行操作,比如获得最大 值,最小值,求和,平均值,统计数量
public void test03(){
// 获取年龄的最大值
Optional<Person> maxAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).collect(Collectors.maxBy((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge() - p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("最大年龄:" + maxAge.get());
// 获取年龄的最小值
Optional<Person> minAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).collect(Collectors.minBy((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge() - p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("最新年龄:" + minAge.get());
// 求所有人的年龄之和
Integer sumAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
)
//.collect(Collectors.summingInt(s -> s.getAge()))
.collect(Collectors.summingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println("年龄总和:" + sumAge);
// 年龄的平均值
Double avgAge = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println("年龄的平均值:" + avgAge);
// 统计数量
Long count = Stream.of(
new Person("张三", 18)
, new Person("李四", 22)
, new Person("张三", 13)
, new Person("王五", 15)
, new Person("张三", 19)
).filter(p->p.getAge() > 18)
.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println("满足条件的记录数:" + count);
}